In this article, I have explained the concept of Serialization and Deserialization of JSON object in C# with an working console application example.
Serialization is an easy way to convert an object to a binary representation that can then be e.g. written to disk or sent over a wire.Serialization is used to export application data into a file. The destination application then uses deserialization to extract the data from the application for further use.
In C#, Serialization is a concept in which, class objects are written or serialized to files. If you have a class named "Students" and the class has 2 properties of ID and Student name.
Serializing can be used to directly write the data properties of the Student class to a file, while Deserialization is used to read the data from the file and construct the Student object again.
You can serialize your own classes if you mark them with [Serializable] attribute. This serializes all members of a class, except those marked as [NonSerialized].
NET offers 2 serializers: binary, SOAP, XML. The difference between binary and SOAP is:
- binary is more efficient (time and memory used)
- binary is not human-readable. SOAP isn’t much better.
XML is slightly different:
- it lives in System.Xml.Serialization
- it uses [XmlIgnore] instead of [NonSerialized] and ignores [Serializable]
- it doesn’t serialize private class members
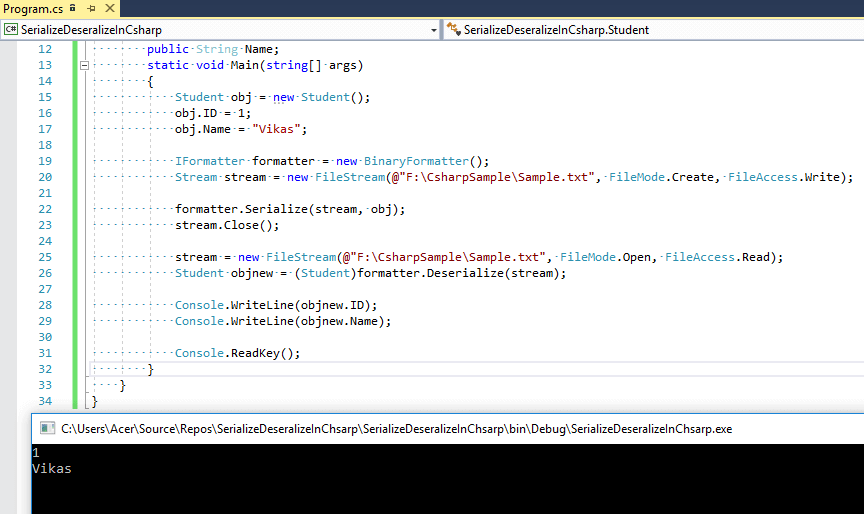
Let's take a look on console application example, in which we have a Class named Student, with properties Id and Name.
You can create a new console application in your Visual Studio, by navigating to "File"-> "New" -> "Project" -> Select "Console app (.NET Framework)" from left pane, and Select "Visual C#" from right pane -> Provide a name "SerializeDeseralizeInCsharp" and then Click "OK"
Once Visual Studio genreates console application Template files, then in your "Program.cs" file use the below code
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
namespace SerializeDeseralizeInCsharp
{
[Serializable]
class Student
{
public int ID;
public String Name;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student obj = new Student();
obj.ID = 1;
obj.Name = "Vikas";
IFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
Stream stream = new FileStream(@"F:\CsharpSample\Sample.txt", FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
formatter.Serialize(stream, obj);
stream.Close();
stream = new FileStream(@"F:\CsharpSample\Sample.txt", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
Student objnew = (Student)formatter.Deserialize(stream);
Console.WriteLine(objnew.ID);
Console.WriteLine(objnew.Name);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
So basically, in the above code, we are
- We create the object "stream" to open the file Sample.txt in reading only mode.
- We then use the formatter class which is used to deserialize the object, which is stored in the Sample.txt file. The object returned is set to the object objnew.
- Finally, we display the properties of the object "objnew" to the console using the "ID" and "name" properties.
Here is the output of the above program when build and executed
That's it, if you have any questions, feel free to ask it below in the below comments section.
You may also like to read:


vikas_jk
Hi
You would have to save the execution details in database with unique id.
Suppose, a user executed a program, you can save that program, it's input/output values in database table.
When they return you show his/her last excuted program by fetching there details from database.
For this either you need user to login/register on your app or website.
If it is console app, you can save data in some file without login, if it website use cookies or JavaScript localstorage to save data without login.