When working with the database, we may sometimes require to fetch data from the database based on certain conditions, in that case, we can use SQL server CASE statement, often referred as Switch case statement in SQL Server, so in this article, I have mentioned what is SQL Server Switch case statement and examples of using SQL Server switch case.
We can also use cursor/loop depending on our requirements but CASE statements are the best alternative to cursor/loop. It evaluates a list of conditions and returns one of the multiple possible result expressions.
You can use CASE expressions anywhere in the SQL Query like CASE expressions can be used within SELECT statement, WHERE clauses, Order by clause, HAVING clauses, & in statements such as SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE and SET.
Table of Contents
Syntax for SQL Case statement
Simple CASE expression:
CASE input_expression
WHEN when_expression THEN result_expression [ ...n ]
[ ELSE else_result_expression ]
END
Searched CASE expression:
CASE
WHEN Boolean_expression
THEN result_expression [ ...n ]
[ ELSE else_result_expression ]
END Where, input_expression is the expression evaluated when the simple CASE format is used while Boolean_expression Is the Boolean expression evaluated when using the searched CASE format. Boolean_expression is any valid Boolean expression.
CASE expression has two formats:
- The simple CASE expression compares an expression to a set of simple expressions to determine the result.
- Syntax:
CASE input_expression WHEN expression_1 THEN Result_1 WHEN expression_2 THEN Result_2 ELSE Result END? - The simple CASE expression operates by comparing the first expression to the expression in each WHEN clause for equivalency. If these expressions are equivalent, the expression in the THEN clause will be returned.
- Example:
DECLARE @TestingCaseExpression INT SET @TestingVal = 3 SELECT CASE @TestingVal WHEN 1 THEN 'First' WHEN 2 THEN 'Second' WHEN 3 THEN 'Third' ELSE 'Other' END?
- Syntax:
- The searched CASE expression evaluates a set of Boolean expressions to determine the result.
- Syntax:
CASE WHEN Boolean_expression_1 THEN Result_1 WHEN Boolean_expression_2 THEN Result_2 ELSE Result END? - It evaluates, in the order specified, Boolean_expression for each WHEN clause & Returns result_N of the first Boolean_expression that evaluates to TRUE.
- Example:
DECLARE @TestingValue INT SET @TestingValue = 5 SELECT CASE WHEN @TestingValue <=3 THEN 'Top 5' ELSE 'Other' END?
- Syntax:
Examples of SQL server switch case statement
Now let's get started with some examples in SQL server switch case using AdventureWorks2012 test database, if you don't have this database you can download and restore AdventureWorks Database, after downloading .bak file of the database from this URL Restore (Import) database from .bak file in SQL server if you have SQL server, else you can download SQL server various version.
Select statement with a simple Case example
USE AdventureWorks2012;
GO
SELECT ProductNumber, Category =
CASE ProductLine
WHEN 'M' THEN 'Mountain'
WHEN 'S' THEN 'Other sale items'
ELSE 'Not for sale'
END,
Name
FROM Production.Product
ORDER BY ProductNumber;
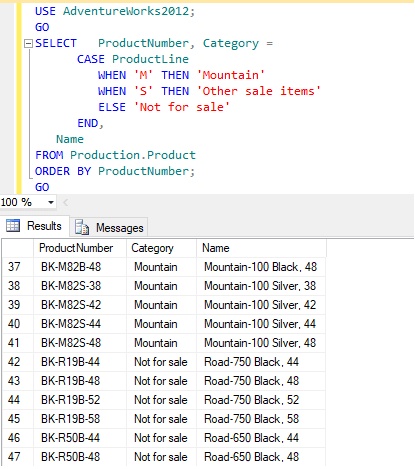
GO the above script is a simple CASE expression allows for only an equality check; no other comparisons are made. The following example uses the CASE expression to change the display of product line categories to make them more understandable.
Here is the output of the above script when executed on my local SQL server
Select statement with searched Case
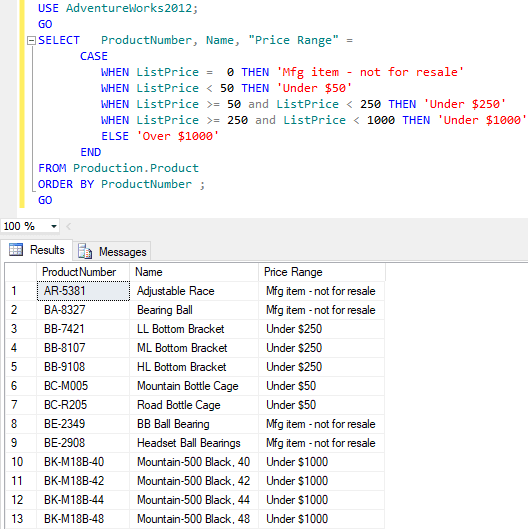
Let's try to use a searched case statement in which we will use the boolean expression, in the below example we will get the list price as a text comment based on the price range for a product.
USE AdventureWorks2012;
GO
SELECT ProductNumber, Name, "Price Range" =
CASE
WHEN ListPrice = 0 THEN 'Mfg item - not for resale'
WHEN ListPrice < 50 THEN 'Under $50'
WHEN ListPrice >= 50 and ListPrice < 250 THEN 'Under $250'
WHEN ListPrice >= 250 and ListPrice < 1000 THEN 'Under $1000'
ELSE 'Over $1000'
END
FROM Production.Product
ORDER BY ProductNumber ;
GO Output:
Case statement with Order By clause
Let's check a simple example of ORDER By clause with case statement in which we will Order data based on conditions, so in the below example script If DeptIp=4 then we are running order by as Descending of FirstName else if DeptId= 3, we are ordering data by Ascending Order of LastName
SELECT * FROM dbo.MyEmployees
ORDER BY
CASE DeptID WHEN '4' THEN FirstName END Desc,
CASE DeptID WHEN '3' THEN LastName END ASC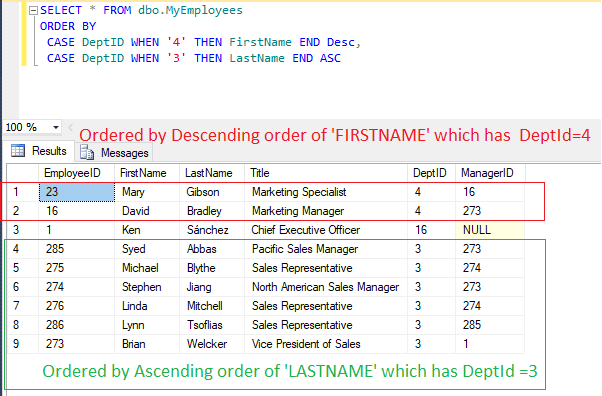
Using CASE in an UPDATE statement
USE AdventureWorks2012;
GO
UPDATE HumanResources.Employee
SET VacationHours =
( CASE
WHEN ((VacationHours - 10.00) < 0) THEN VacationHours + 40
ELSE (VacationHours + 20.00)
END
)
OUTPUT Deleted.BusinessEntityID, Deleted.VacationHours AS BeforeValue,
Inserted.VacationHours AS AfterValue
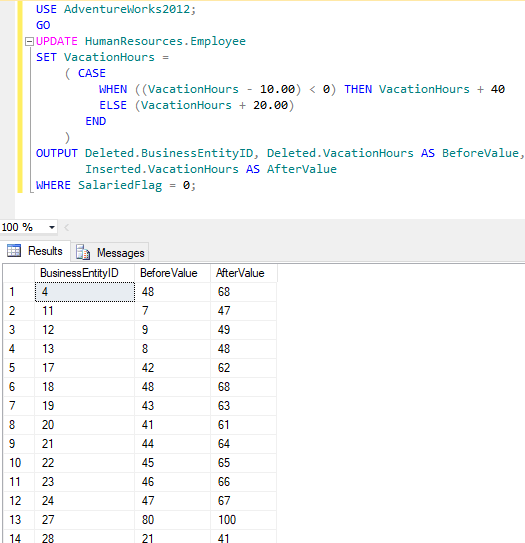
WHERE SalariedFlag = 0; In the above script, we are using the CASE expression in an UPDATE statement to determine the value that is set for the column VacationHours for employees with SalariedFlag set to 0. When subtracting 10 hours from VacationHours results in a negative value, VacationHours is increased by 40 hours; otherwise, VacationHours is increased by 20 hours.
Output:
Having Clause with CASE expression
USE AdventureWorks2012;
GO
SELECT JobTitle, MAX(ph1.Rate)AS MaximumRate
FROM HumanResources.Employee AS e
JOIN HumanResources.EmployeePayHistory AS ph1
ON e.BusinessEntityID = ph1.BusinessEntityID
GROUP BY JobTitle
HAVING (MAX(CASE WHEN Gender = 'M'
THEN ph1.Rate
ELSE NULL END) > 80.00
OR MAX(CASE WHEN Gender = 'F'
THEN ph1.Rate
ELSE NULL END) > 60.00)
ORDER BY MaximumRate DESC; The above SQL query returns the maximum hourly rate for each job title in the
HumanResources.Employee table. The HAVING clause restricts the titles to those that are held by men with a maximum pay rate greater than 80 dollars or women with a maximum pay rate greater than 60 dollars.
.png)
You may also like:
Aggregate Functions in SQL Server (SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX)
If you need more Case statement example you can find it here & if you have any questions related to above article, feel free to ask it below in comment's section.
