In the previous article, I have explained Linked list & linked list program in C with Algorithm, so if you want to learn about the linked list in details, you can read that article, before proceeding to this one.
Sorting linked list program in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node * next;
};
// decalre all functions
struct node * start = NULL;
struct node * create_ll(struct node * );
struct node * display(struct node * );
struct node *sort_list(struct node *);
void main() {
int option;
do {
printf("\n\n *****MAIN MENU *****");
printf("\n 1: Create a list");
printf("\n 2: Display the list");
printf("\n 3: Sort linked list");
printf("\n 4: EXIT");
printf("\n\n Enter your option : ");
scanf("%d", &option);
switch (option) {
case 1:
start = create_ll(start);
printf("\n Linked List Created");
break;
case 2:
start = display(start);
break;
case 3:
printf("\n Sorted linked list data");
start = sort_list(start);
break;
}
} while (option != 4);
getch();
}
//Create linked list function
//it will keep asking for data until -1 is entered
struct node * create_ll(struct node * start) {
struct node * new_node, * ptr;
int num;
printf("\n Enter -1 to end");
printf("\n Enter the data: ");
scanf("%d", & num);
while (num != -1) {
new_node = (struct node * ) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
new_node -> data = num;
if (start == NULL) {
new_node -> next = NULL;
start = new_node;
} else {
ptr = start;
while (ptr -> next != NULL)
ptr = ptr -> next;
ptr -> next = new_node;
new_node -> next = NULL;
}
printf("\n Enter the data : ");
scanf("%d", & num);
}
return start;
}
//display linked list data
//after looping it from start until NULL
struct node * display(struct node * start) {
struct node * ptr;
ptr = start;
while (ptr != NULL) {
printf("\t %d", ptr -> data);
ptr = ptr -> next;
}
return start;
}
//sorting linked list code
struct node *sort_list(struct node *start)
{
struct node *ptr1, *ptr2;
int temp;
ptr1 = start;
while(ptr1 -> next != NULL)
{
ptr2 = ptr1 -> next;
while(ptr2 != NULL)
{
if(ptr1 -> data > ptr2 -> data)
{
temp = ptr1 -> data;
ptr1 -> data = ptr2 -> data;
ptr2 -> data = temp;
}
ptr2 = ptr2 -> next;
}
ptr1 = ptr1 -> next;
}
return start; // Had to be added
}In above code, to sort linked list, we are ptr -> data to compare adjacent values, if left value is greater than right, we interchange the positions.
We are following this procedure for complete list by using while loop.
Output: (https://onlinegdb.com/rJboZt6l7)
*****MAIN MENU *****
1: Create a list
2: Display the list
3: Sort linked list
4: EXIT
Enter your option : 1
Enter -1 to end
Enter the data: 22
Enter the data : 6
Enter the data : 8
Enter the data : 45
Enter the data : -1
Linked List Created
*****MAIN MENU *****
1: Create a list
2: Display the list
3: Sort linked list
4: EXIT
Enter your option : 2
22 6 8 45
*****MAIN MENU *****
1: Create a list
2: Display the list
3: Sort linked list
4: EXIT
Enter your option : 3
Sorted linked list data
*****MAIN MENU *****
1: Create a list
2: Display the list
3: Sort linked list
4: EXIT
Enter your option : 2
6 8 22 45
*****MAIN MENU *****
1: Create a list
2: Display the list
3: Sort linked list
4: EXIT
Enter your option : 4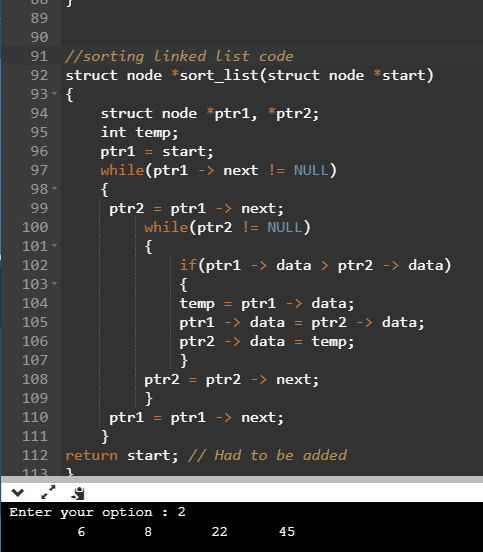
You may also like:
Linked list program in C (Algorithm & Code sample)
That's it, as you can see first we are creating the linked list and then sorting it.
